|
|
||
|
|
||
|
Consider a ball thrown straight up and suppose it is caught by thrower after exactly 2 seconds.
h = height in feet of the ball
h = 0 is the heigth of throwing hand
t = time in seconds
In general, we learn from physics that
h(t) = a + bt - 16 t2
h(0) = h(2) = 0 implies a = 0 and b = 32
hence
h(t) = 32t - 16 t2
We calculate the average velocity during different time intervals:
Average velocity during the first second =![]() =16
ft / s
=16
ft / s
Average velocity during the first 1 / 10 th second
=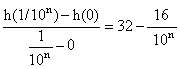
approaches 32 ft / s as n increases to infinity.
Thus the instantaneous velocity at t = 0 is 32 ft / s.